Cardiovascular (CV) healthcare delivery has seen remarkable advancements over the years due to numerous digital health innovations aimed at enhancing the quality and consistency of care. While these solutions offer many benefits to CV patients and providers, they also require clinicians to embrace and depend upon evolving technologies increasingly.
As such, health systems are regularly tasked with integrating technologies and information systems into their electronic health records (EHRs) and how to promote provider-friendly and efficient workflows, particularly when integrations aren’t seamless.
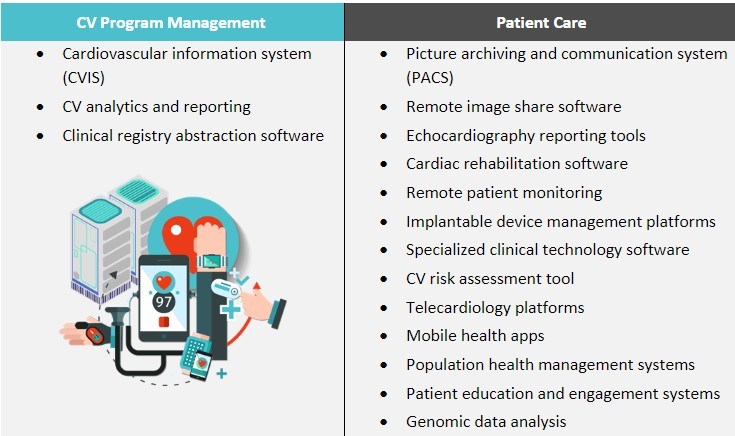
Figure 1: Common CV IT Solutions and Systems
Potential Challenges and Solutions
Technologies capable of improving CV providers’ workflows and ability to care for patients efficiently across care settings require a lot of thought to operationalize. Navigating the complexities of interoperability within CV care requires addressing issues such as disparate data formats, communication protocol variations, and data silos. Highlighted below are nine typical digital challenges health systems encounter as they strive to provide comprehensive CV services to their patients.
1. Proliferation of Third-Party Digital Solutions
Challenge: The explosion of specialized CV digital solutions has led to an array of third-party systems that must be integrated into the EHR. Because hospitals often use separate solutions for EHR, PACS, CVIS, and more, integrating these solutions can be a formidable task
Solution: Consider consolidating solutions into fewer, more robust platforms. For example, a single CVIS solution that supports all modalities (e.g., Merge Cardio, syngo Dynamics, and IntelliSpace Cardiovascular) offers better internal integration for CV care and standardized results than a collage of applications.
2. Data Silos and Incomplete Patient Record
Challenge: Fragmented systems result in data silos, where critical patient information is scattered across various platforms. As a result, healthcare providers may not have a comprehensive view of a patient’s CV history and diagnostic data, leading to suboptimal decision-making and, potentially, compromised patient care.
Solution: Develop comprehensive data governance policies and procedures to ensure data consistency and quality. Establish standards for data sharing and management to prevent data silos.
3. Workflow Disruptions
Challenge: Fragmentation disrupts clinical workflows. Navigating multiple systems causes providers to lose valuable time.
Solution: Invest in comprehensive training and superuser support to help healthcare professionals stay up to date with functionalities and find efficiencies across integrated systems.
4. Increased Risk of Errors
Challenge: The manual entry of data between disparate systems increases the risk of errors and discrepancies. This not only affects patient care but adds to administrative burden and provider burnout.
Solution: Incorporate automation within existing workflows and processes to reduce the need to manually transfer data between systems.
5. Cost Implications
Challenge: Integrating third-party solutions can be costly in terms of time, resources, and finances. Hospitals may need to hire specialized IT staff or engage in lengthy customization efforts, potentially straining budgets.
Solution: Create a strategic plan for IT integration that outlines objectives and budgets. Prioritize integration initiatives based on their potential impact on patient care and operational efficiency.
6. Compliance
Challenge: Ensuring data security and patient privacy across a fragmented ecosystem is complex, raising concerns about compliance with healthcare regulations.
Solution: Include quality and compliance stakeholders in IT governance, especially for significant workflow updates. Establish and maintain processes to regularly audit systems for compliance.
7. Limited Data Analytics
Challenge: Meaningful data analytics play a crucial role in improving efficiencies and patient outcomes. Fragmented data hinders comprehensive analysis and reporting, limiting the insights that can be derived from the information collected.
Solution: Identify key sources of data, and target the reconciliation of all patient information within the EHR. Optimize reporting by determining the relevant capabilities of new products and integrating outputs.
8. Integration
Challenge: While several standardized data formats and communication protocols exist, integration can still be complicated due to the many device and software vendors required for CV care.
Solution: Ensure vendor selection is a key part of your health system’s overall integration strategy. The IT platforms chosen must support the quick and seamless transfer of information where it’s needed, when it’s needed, especially across the EHR, CVIS, and PACS.
9. Resistance to Change
Challenge: Healthcare professionals have historically been reluctant to adopt new technologies or alter established workflows. Overcoming this resistance and gaining buy-in for integration initiatives can be a hurdle.
Solution: Implement effective change management strategies to overcome resistance to IT integration. Involve key stakeholders in decision-making, and communicate the benefits of integrated systems.
The hurdles associated with integrating third-party CV IT solutions are significant but not insurmountable, and system leaders should prioritize addressing them, as the benefits of a high-performing system outweigh the challenges. By strategically planning integration initiatives, collaborating with vendors, and prioritizing interoperability, healthcare organizations can create a more cohesive and efficient CV IT ecosystem that fulfills the needs of both patients and providers.
About ECG
ECG’s IT strategy and CV consulting experts are passionate about improving care delivery and since 2010 have conducted nearly 300 engagements across more than 100 parent companies.
Edited by: Emily Johnson


